Robotics Innovations: Transforming U.S. Logistics by 2025

Three pivotal robotics innovations, extending beyond conventional self-driving cars, are set to significantly redefine and optimize U.S. logistics operations by 2025, enhancing efficiency, safety, and scalability across the supply chain.
While much of the public’s attention on automation in transportation has focused on self-driving cars, a quieter, yet profound, revolution is underway within the U.S. logistics sector. By 2025, three specific robotics innovations are poised to dramatically reshape how goods are moved, stored, and delivered across the nation. This transformation goes far beyond self-driving cars: 3 robotics innovations transforming U.S. logistics by 2025 are not just incremental improvements but fundamental shifts in operational paradigms.
The Rise of Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) in Warehousing
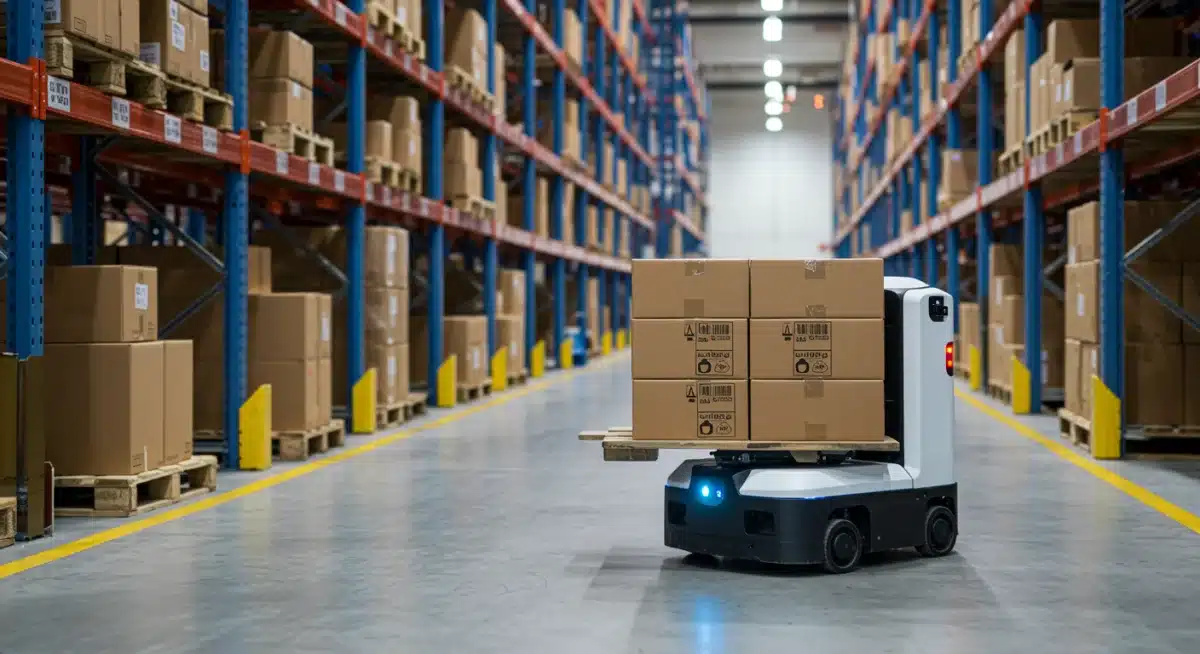
Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) are rapidly becoming the backbone of modern warehousing, offering unprecedented flexibility and efficiency in material handling. Unlike their Automated Guided Vehicle (AGV) predecessors, AMRs do not require fixed paths or magnetic strips, allowing them to navigate dynamic environments intelligently.
Their ability to interpret their surroundings and adapt to changes in real-time makes them indispensable for optimizing warehouse layouts and workflows. These robots are not merely transporting items; they are fundamentally altering the speed and accuracy with which orders are fulfilled and inventory is managed.
Enhanced Navigation and Collaboration
One of the most significant advancements in AMR technology is their sophisticated navigation systems, often powered by AI and machine learning. This allows them to avoid obstacles, find the most efficient routes, and even collaborate with other robots and human workers seamlessly. This collaborative capability is crucial for maximizing throughput in high-volume distribution centers.
- Dynamic Path Planning: AMRs can recalculate routes on the fly, bypassing congested areas or unexpected obstructions.
- Human-Robot Interaction: Designed to operate safely alongside humans, improving overall workplace safety.
- Scalability: Fleets of AMRs can be easily expanded or contracted based on demand fluctuations.
Impact on Labor and Efficiency
The integration of AMRs directly addresses labor shortages and increases operational efficiency. By automating repetitive tasks like picking, sorting, and transporting, human workers can be reallocated to more complex, value-added roles. This not only boosts productivity but also reduces the physical strain on employees, leading to a safer and more ergonomic work environment. The data collected by AMRs also provides valuable insights into warehouse performance, allowing for continuous optimization.
In conclusion, AMRs are not just automated carts; they are intelligent, adaptable systems that are revolutionizing warehousing by enhancing efficiency, improving safety, and offering scalable solutions to meet the evolving demands of the U.S. logistics landscape.
Drone Delivery Systems: The Last-Mile Frontier
Beyond the confines of warehouses, drone delivery systems are emerging as a game-changer for the last mile of logistics. While still facing regulatory hurdles and public perception challenges, the technological advancements in drone capabilities are undeniable. These aerial robots promise faster, more economical, and environmentally friendly delivery options, especially for smaller packages and urgent shipments.
The potential for drones to bypass urban traffic congestion and reach remote areas efficiently positions them as a critical component in future logistics networks. Companies are investing heavily in developing robust, safe, and scalable drone fleets capable of navigating complex urban and rural environments.
Overcoming Operational Challenges
Successful drone delivery relies on sophisticated software for flight planning, obstacle avoidance, and package release. Battery life, payload capacity, and adverse weather conditions remain significant operational challenges that engineers are actively addressing. The development of drone charging stations and advanced battery technologies are key areas of innovation.


- Advanced Navigation: GPS, computer vision, and AI for precise, autonomous flight.
- Increased Payload: Innovations in drone design are boosting carrying capacity for various package sizes.
- Regulatory Frameworks: Collaborative efforts between industry and government to establish safe operating guidelines.
Economic and Environmental Advantages
From an economic standpoint, drones can significantly reduce delivery costs by minimizing fuel consumption and labor expenses associated with traditional vehicle-based deliveries. Environmentally, electric drones offer a zero-emission alternative, contributing to greener logistics practices. This dual benefit makes drone delivery an attractive prospect for companies looking to optimize both their bottom line and their environmental footprint.
In summary, drone delivery systems are poised to revolutionize last-mile logistics by offering speed, cost-efficiency, and environmental benefits, despite the ongoing challenges in technological and regulatory development.
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) for Supply Chain Management
While not physical robots, Robotic Process Automation (RPA) plays a crucial role in the broader robotics transformation of U.S. logistics. RPA involves using software robots (bots) to automate repetitive, rule-based tasks traditionally performed by humans in back-office operations. In supply chain management, RPA can streamline everything from order processing and inventory tracking to supplier communication and data analysis.
By automating these administrative functions, RPA frees up human resources to focus on strategic decision-making and problem-solving. This leads to faster processing times, reduced errors, and greater overall operational agility, directly impacting the efficiency and responsiveness of the entire logistics network.
Streamlining Administrative Workflows
RPA bots can interact with various systems and applications, mimicking human actions to complete tasks. This includes data entry, invoice processing, email communication, and report generation. The ability of RPA to integrate disparate systems without complex API development makes it a highly flexible and cost-effective automation solution for many logistics companies.
- Order Processing: Automating the entry and verification of customer orders, reducing manual errors.
- Inventory Management: Automatically updating stock levels and triggering reorders based on predefined rules.
- Freight Auditing: Reviewing and approving freight invoices for accuracy, identifying discrepancies.
Data Accuracy and Decision Support
The precision of RPA significantly reduces the human error factor in administrative tasks, leading to higher data accuracy. This improved data quality is vital for informed decision-making in supply chain management. By providing clean, real-time data, RPA supports advanced analytics and predictive modeling, enabling logistics professionals to anticipate demands, optimize routes, and manage risks more effectively.
Ultimately, RPA is transforming supply chain management by automating routine administrative tasks, improving data accuracy, and providing critical support for strategic decision-making, thus enhancing the overall efficiency and resilience of logistics operations.
Comparative Analysis: AMRs vs. Drones vs. RPA
Understanding the distinct roles and synergistic potential of these three robotics innovations is key to grasping their collective impact on U.S. logistics. While AMRs focus on internal warehouse efficiency, drones tackle the external last-mile challenge, and RPA optimizes the administrative backbone of the entire supply chain.
Each technology addresses specific pain points within the logistics ecosystem, yet their combined deployment offers a holistic approach to automation. For example, RPA can manage inventory data that informs AMR movements, while drone delivery schedules can be optimized through RPA-driven analytics.
Synergies and Interdependencies
The true power of these innovations lies in their ability to work together. A fully integrated logistics system might see RPA managing incoming orders, triggering AMRs to pick and stage products, and then coordinating drone dispatches for final delivery. This seamless flow of information and physical goods creates an optimized, end-to-end supply chain.
- Integrated Data Flow: RPA provides the data backbone for both AMR and drone operations.
- Optimized Operations: Each technology addresses a different segment, leading to comprehensive efficiency gains.
- Future-Proofing: Combined, they offer a resilient and adaptable logistics infrastructure against future disruptions.
Challenges and Adoption Rates
While the benefits are clear, adoption rates vary. AMRs are seeing rapid deployment due to their immediate ROI and relatively contained operational environments. Drones face more significant regulatory and public acceptance hurdles, making their widespread adoption slower. RPA, being software-based, often has a lower barrier to entry and is being adopted across various industries, including logistics, for its quick implementation and efficiency gains.
In conclusion, a comparative analysis reveals that while AMRs, drones, and RPA each offer unique benefits, their combined, synergistic application holds the greatest promise for a truly transformed and efficient U.S. logistics sector by 2025.
The Economic and Societal Impact by 2025
The widespread adoption of these robotics innovations is projected to have a profound economic and societal impact on the U.S. logistics sector by 2025. Economically, companies can expect significant cost reductions in labor, fuel, and operational overhead, leading to increased profitability and competitiveness. The enhanced efficiency also means faster delivery times, meeting growing consumer expectations for instant gratification.
Societally, the transformation will lead to shifts in the labor market. While some jobs may be automated, new roles will emerge in robotics management, maintenance, and data analysis. The increased speed and reliability of logistics will also support a more robust economy, ensuring goods are available when and where they are needed.
Job Creation and Reskilling
The narrative often focuses on job displacement, but the reality is more nuanced. Automation creates a demand for new skills and new types of jobs. Logistics companies will need robotics engineers, data scientists, AI specialists, and technicians to manage and maintain these advanced systems. This necessitates significant investment in reskilling programs for the existing workforce.
- New Skill Sets: Demand for robotics technicians, AI specialists, and data analysts will grow.
- Workforce Retraining: Programs to equip existing employees with necessary technological skills.
- Higher-Value Roles: Human workers can transition to more strategic and creative tasks.
Supply Chain Resilience and Sustainability
Beyond efficiency, these robotics innovations contribute significantly to supply chain resilience. Automated systems are less susceptible to human error, labor shortages, or disruptions like pandemics. This ensures a more stable and predictable flow of goods. Furthermore, the shift towards electric drones and optimized routes reduces the carbon footprint of logistics, aligning with global sustainability goals.
Ultimately, by 2025, these robotics innovations will not only drive economic growth through efficiency and cost savings but also foster a more resilient, sustainable, and adaptable logistics ecosystem, while simultaneously reshaping the nature of work within the industry.
Navigating the Future: Challenges and Opportunities
The path to a fully automated logistics future is not without its challenges. Technical hurdles, such as battery limitations for drones or complex integration issues for AMRs, require continuous innovation. Regulatory frameworks need to evolve rapidly to keep pace with technological advancements, especially concerning drone airspace management and data privacy.
However, these challenges also present significant opportunities for companies that are agile and forward-thinking. Early adopters stand to gain a competitive advantage, while innovators can carve out new market niches by developing solutions to address current limitations. The collaborative effort between technology developers, logistics providers, and regulatory bodies will be crucial for successful implementation.
Addressing Security and Data Privacy
The increasing reliance on automated systems and data-driven operations raises concerns about cybersecurity and data privacy. Protecting sensitive logistics data from breaches and ensuring the secure operation of robotic systems will be paramount. Robust cybersecurity protocols and ethical data handling practices must be integrated into every stage of development and deployment.
- Cybersecurity Protocols: Implementing strong defenses against hacking and data theft.
- Data Governance: Establishing clear policies for data collection, usage, and storage.
- Ethical AI: Ensuring algorithms are fair and unbiased in their decision-making processes.
Investment and Infrastructure Development
Significant investment will be required in both technology and infrastructure to support the widespread adoption of these robotics innovations. This includes upgrading warehouses, developing drone charging networks, and investing in advanced IT systems for RPA integration. Government incentives and public-private partnerships can play a vital role in accelerating this infrastructure development.
In conclusion, while the future of robotics in U.S. logistics presents challenges related to technology, regulation, and security, it also unlocks immense opportunities for those willing to invest and innovate, ultimately leading to a more efficient, resilient, and sustainable supply chain.
| Innovation | Key Impact by 2025 |
|---|---|
| Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) | Revolutionize warehouse efficiency, reducing manual labor and optimizing internal transport. |
| Drone Delivery Systems | Transform last-mile delivery, offering speed, cost-effectiveness, and environmental benefits. |
| Robotic Process Automation (RPA) | Streamline administrative supply chain tasks, boosting data accuracy and operational agility. |
| Integrated Robotics | Combined deployment creates a holistic, resilient, and highly efficient logistics ecosystem. |
Frequently Asked Questions About Robotics in Logistics
AMRs (Autonomous Mobile Robots) navigate intelligently using sensors and AI, dynamically adapting to their environment without fixed paths. AGVs (Automated Guided Vehicles), conversely, follow predefined routes, often marked by wires or magnetic strips, offering less flexibility in dynamic warehouse settings.
Drone delivery promises faster last-mile delivery, especially in congested urban areas or remote locations. It also offers significant cost reductions by minimizing fuel and labor expenses, alongside environmental benefits from using electric, zero-emission vehicles. This enhances overall delivery efficiency and sustainability.
While RPA automates administrative tasks, its impact on physical logistics is indirect yet profound. By streamlining order processing, inventory management, and data analysis, RPA ensures that physical robots like AMRs and drones receive accurate, timely instructions, thereby optimizing the entire logistical workflow and decision-making for physical movements.
Key challenges include developing robust regulatory frameworks, especially for drone operations, ensuring cybersecurity for integrated systems, and managing the initial investment costs. Workforce reskilling and public acceptance are also crucial factors that need to be addressed for seamless and widespread adoption.
While some repetitive tasks may be automated, robotics will create new jobs in areas such as robot maintenance, data analysis, and system management. The focus will shift towards higher-skilled roles, necessitating workforce retraining and fostering a more technologically adept logistics professional.
Conclusion
The U.S. logistics landscape is undergoing a profound transformation, driven by innovations far beyond the public gaze on self-driving vehicles. Autonomous Mobile Robots, advanced drone delivery systems, and Robotic Process Automation are not just futuristic concepts; they are rapidly becoming integral components of a more efficient, resilient, and sustainable supply chain. By 2025, these technologies will collectively redefine operational standards, optimize resource allocation, and reshape the nature of work within the industry. Companies that embrace these advancements will not only gain a significant competitive edge but also contribute to a more robust and responsive global economy.